Set-DnsServerClientSubnet
Set-DnsServerClientSubnet is accessible with the help of DnsServer module. To configure DnsServer, go through this link.
Synopsis
Updates the IP addresses in a client subnet.
Description
The Set-DnsServerClientSubnet cmdlet updates the IP addresses in a client subnet on a Domain Name System (DNS) server. You can add, remove, or replace addresses. You can modify the IPv4 addresses, IPv6 addresses, or both kinds of addresses.
Parameters
-Action
Specifies whether to add to, remove, or replace the IP addresses in the client subnet. The acceptable values for this parameter are:
- ADD
- REMOVE
- REPLACE
| Type: | String |
| Accepted values: | ADD, REMOVE, REPLACE |
| Position: | 2 |
| Default value: | None |
| Accept pipeline input: | False |
| Accept wildcard characters: | False |
-AsJob
Runs the cmdlet as a background job. Use this parameter to run commands that take a long time to complete.
The cmdlet immediately returns an object that represents the job and then displays the command prompt. You can continue to work in the session while the job completes. To manage the job, use the *-Job cmdlets. To get the job results, use the Receive-Job cmdlet.
| Type: | SwitchParameter |
| Position: | Named |
| Default value: | None |
| Accept pipeline input: | False |
| Accept wildcard characters: | False |
-CimSession
Runs the cmdlet in a remote session or on a remote computer. Enter a computer name or a session object, such as the output of a New-CimSession or Get-CimSession cmdlet. The default is the current session on the local computer.
| Type: | CimSession[] |
| Aliases: | Session |
| Position: | Named |
| Default value: | None |
| Accept pipeline input: | False |
| Accept wildcard characters: | False |
-ComputerName
Specifies a remote DNS server. You can specify an IP address or any value that resolves to an IP address, such as a fully qualified domain name (FQDN), host name, or NETBIOS name.
| Type: | String |
| Aliases: | Cn |
| Position: | Named |
| Default value: | None |
| Accept pipeline input: | False |
| Accept wildcard characters: | False |
-Confirm
Prompts you for confirmation before running the cmdlet.
| Type: | SwitchParameter |
| Aliases: | cf |
| Position: | Named |
| Default value: | False |
| Accept pipeline input: | False |
| Accept wildcard characters: | False |
-IPv4Subnet
Specifies an array IPv4 subnet addresses in Classless Interdomain Routing (CIDR) notation.
| Type: | String[] |
| Position: | 3 |
| Default value: | None |
| Accept pipeline input: | True |
| Accept wildcard characters: | False |
-IPv6Subnet
Specifies an array IPv6 subnet addresses in CIDR notation.
| Type: | String[] |
| Position: | 4 |
| Default value: | None |
| Accept pipeline input: | True |
| Accept wildcard characters: | False |
-Name
Specifies the name of the client subnet to modify.
| Type: | String |
| Position: | 1 |
| Default value: | None |
| Accept pipeline input: | True |
| Accept wildcard characters: | False |
-PassThru
Returns an object representing the item with which you are working. By default, this cmdlet does not generate any output.
| Type: | SwitchParameter |
| Position: | Named |
| Default value: | None |
| Accept pipeline input: | False |
| Accept wildcard characters: | False |
-ThrottleLimit
Specifies the maximum number of concurrent operations that can be established to run the cmdlet. If this parameter is omitted or a value of 0 is entered, then Windows PowerShell calculates an optimum throttle limit for the cmdlet based on the number of CIM cmdlets that are running on the computer. The throttle limit applies only to the current cmdlet, not to the session or to the computer.
| Type: | Int32 |
| Position: | Named |
| Default value: | None |
| Accept pipeline input: | False |
| Accept wildcard characters: | False |
-WhatIf
Shows what would happen if the cmdlet runs. The cmdlet is not run.
| Type: | SwitchParameter |
| Aliases: | wi |
| Position: | Named |
| Default value: | False |
| Accept pipeline input: | False |
| Accept wildcard characters: | False |
Syntax
Set-DnsServerClientSubnet [-Name] <String> [[-IPv4Subnet] <String[]>] [[-IPv6Subnet] <String[]>] [-Action] <String> [-PassThru] [-ComputerName <String>] [-CimSession <CimSession[]>] [-ThrottleLimit <Int32>] [-AsJob] [-WhatIf] [-Confirm] [<CommonParameters>]
—————EXAMPLE 1—————
Add an IPv4 address to a client subnet
PS C:>Add-DnsServerClientSubnet -Name “MumbaiSubnet” -IPv6Subnet 0db8::1/28 -PassThru -IPv4Subnet 192.182.1.1/8
PS C:> Set-DnsServerClientSubnet -Name “MumbaiSubnet” -Action ADD -IPv4Subnet 192.168.10.4/16 -PassThru | Format-List
The first command creates a client subnet named MumbaiSubnet by using the Add-DnsServerClientSubnet cmdlet.
The second command adds an IPv4 subnet to the MumbaiSubnet client subnet. The command uses the Format-List cmdlet to control the appearance of the output.
The command includes the PassThru parameter. The added IPv4 address appears in the computer output.
—————EXAMPLE 2—————
Replace an IPv6 address in a client subnet
PS C:\>Add-DnsServerClientSubnet -Name “AsiaSubnet” -IPv6Subnet 0db8::1/28 -PassThru -IPv4Subnet 192.168.1.1/8
PS C:\> Set-DnsServerClientSubnet -Name “AsiaSubnet” -Action REPLACE -IPv6Subnet 0db8::1/8 -PassThru | Format-List
The first command creates a client subnet named AsiaSubnet that includes the IPv6 address 0db8::1/28.
The second command replaces the IPv6 addresses for the client subnet. The computer output includes the address 0db8::1/8 in place of 0db8::1/28.
—————EXAMPLE 3—————
Remove an IPv4 address from a client subnet
PS C:\>Add-DnsServerClientSubnet -Name “AsiaSubnet” -IPv6Subnet 0db8::1/28 -PassThru -IPv4Subnet 192.168.1.1/8
PS C:\> Set-DnsServerClientSubnet -Name “AsiaSubnet” -Action REMOVE -IPv4Subnet 192.168.1.1/8 -PassThru | Format-List
The first command creates a client subnet named AsiaSubnet that includes both an IPv4 address and an IPv6 address.
The second command removes the IPv4 address. The computer output displays only the IPv6 address.
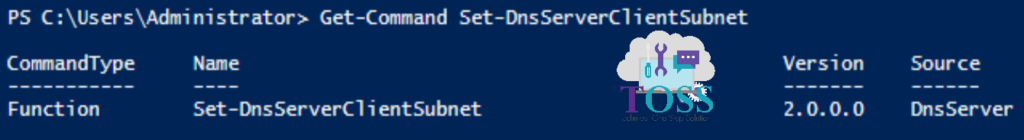
You can check the Version, CommandType and Source of this cmdlet by giving below command.
Get-Command Set-DnsServerClientSubnet
You can also read about
- Add-DnsServerClientSubnet
- Get-DnsServerClientSubnet
- Remove-DnsServerClientSubnet
To know more PowerShell cmdlets(Commands) on DnsServer click here