Add-DnsServerStubZone
Add-DnsServerStubZone is accessible with the help of DnsServer module. To configure DnsServer, go through this link.
Synopsis
Adds a DNS stub zone.
Description
The Add-DnsServerStubZone cmdlet adds a stub zone. A stub zone is a copy of a Domain Name System (DNS) zone that contains only resource records that identify the DNS servers for that zone.
You can add either a forward lookup zone or a reverse lookup zone. You can add either an Active Directory-integrated zone or a file-backed zone.
Parameters
-AsJob
Runs the cmdlet as a background job. Use this parameter to run commands that take a long time to complete.
The cmdlet immediately returns an object that represents the job and then displays the command prompt. You can continue to work in the session while the job completes. To manage the job, use the *-Job cmdlets. To get the job results, use the Receive-Job cmdlet.
| Type: | SwitchParameter |
| Position: | Named |
| Default value: | None |
| Accept pipeline input: | False |
| Accept wildcard characters: | False |
-CimSession
Runs the cmdlet in a remote session or on a remote computer. Enter a computer name or a session object, such as the output of a New-CimSession or Get-CimSession cmdlet. The default is the current session on the local computer.
| Type: | CimSession[] |
| Aliases: | Session |
| Position: | Named |
| Default value: | None |
| Accept pipeline input: | False |
| Accept wildcard characters: | False |
-ComputerName
Specifies a DNS server. If you do not specify this parameter, the command runs on the local system. You can specify an IP address or any value that resolves to an IP address, such as a fully qualified domain name (FQDN), host name, or NETBIOS name.
| Type: | String |
| Aliases: | Cn |
| Position: | Named |
| Default value: | None |
| Accept pipeline input: | False |
| Accept wildcard characters: | False |
-Confirm
Prompts you for confirmation before running the cmdlet.
| Type: | SwitchParameter |
| Aliases: | cf |
| Position: | Named |
| Default value: | False |
| Accept pipeline input: | False |
| Accept wildcard characters: | False |
-DirectoryPartitionName
Specifies a directory partition on which to store the zone. Use this parameter when the ReplicationScope parameter has a value of Custom.
| Type: | String |
| Position: | 4 |
| Default value: | None |
| Accept pipeline input: | True |
| Accept wildcard characters: | False |
-LoadExisting
Indicates that the server loads an existing file for the zone. Otherwise, the cmdlet creates default zone records automatically. This switch is relevant only for file-backed zones.
| Type: | SwitchParameter |
| Position: | Named |
| Default value: | None |
| Accept pipeline input: | True |
| Accept wildcard characters: | False |
-MasterServers
Specifies an array of IP addresses of the master servers of the zone. You can use both IPv4 and IPv6.
| Type: | IPAddress[] |
| Position: | 2 |
| Default value: | None |
| Accept pipeline input: | True |
| Accept wildcard characters: | False |
-Name
Specifies a name of a zone.
| Type: | String |
| Aliases: | ZoneName |
| Position: | 1 |
| Default value: | None |
| Accept pipeline input: | True |
| Accept wildcard characters: | False |
-NetworkId
Specifies a network ID and prefix length for a reverse lookup zone. Use the format A.B.C.D/prefix for IPv4 or 1111:2222:3333:4444::/prefix for IPv6.
For IPv4, the cmdlet creates only class A, B, C, or D reverse lookup zones. If you specify a prefix that is between classes, the cmdlet uses the longer prefix that is divisible by 8. For example, a value of 10.2.10.0/23 adds the 10.2.10.0/24 reverse lookup zone, and the 10.2.11.0/24 reverse lookup zone is not created. If you enter an IPv4 prefix longer than /24, the cmdlet creates a /32 reverse lookup zone.
For IPv6, the cmdlet creates ip6.arpa zones for prefixes from /16 to /128 that are divisible by 4. If you specify a prefix that is between values, the cmdlet uses the longer prefix that is divisible by 4. For example, entering a value of AAAA::/58 adds the AAAA::/60 ip6.arpa zone. If you do not enter a prefix, the cmdlet uses a default prefix value of /128.
| Type: | String |
| Position: | Named |
| Default value: | None |
| Accept pipeline input: | True |
| Accept wildcard characters: | False |
-PassThru
Returns an object representing the item with which you are working. By default, this cmdlet does not generate any output.
| Type: | SwitchParameter |
| Position: | Named |
| Default value: | None |
| Accept pipeline input: | False |
| Accept wildcard characters: | False |
-ReplicationScope
Specifies a partition on which to store an Active Directory-integrated zone. The acceptable values for this parameter are:
- Custom. Any custom directory partition that a user creates. Specify a custom directory partition by using the DirectoryPartitionName parameter.
- Domain. The domain directory partition.
- Forest. The ForestDnsZone directory partition.
- Legacy. A legacy directory partition.
| Type: | String |
| Accepted values: | Forest, Domain, Legacy, Custom |
| Position: | 3 |
| Default value: | None |
| Accept pipeline input: | True |
| Accept wildcard characters: | False |
-ThrottleLimit
Specifies the maximum number of concurrent operations that can be established to run the cmdlet. If this parameter is omitted or a value of 0 is entered, then Windows PowerShell calculates an optimum throttle limit for the cmdlet based on the number of CIM cmdlets that are running on the computer. The throttle limit applies only to the current cmdlet, not to the session or to the computer.
| Type: | Int32 |
| Position: | Named |
| Default value: | None |
| Accept pipeline input: | False |
| Accept wildcard characters: | False |
-WhatIf
Shows what would happen if the cmdlet runs. The cmdlet is not run.
| Type: | SwitchParameter |
| Aliases: | wi |
| Position: | Named |
| Default value: | False |
| Accept pipeline input: | False |
| Accept wildcard characters: | False |
-ZoneFile
Specifies a name of the zone file. This parameter is only relevant for file-backed DNS.
| Type: | String |
| Position: | Named |
| Default value: | None |
| Accept pipeline input: | True |
| Accept wildcard characters: | False |
Syntax
Add-DnsServerStubZone [-LoadExisting] [-MasterServers] <IPAddress[]> [-ComputerName <String>] [-PassThru] [-Name] <String> [-ZoneFile <String>] [-CimSession <CimSession[]>] [-ThrottleLimit <Int32>] [-AsJob] [-WhatIf] [-Confirm] [<CommonParameters>]
Add-DnsServerStubZone [-LoadExisting] [-MasterServers] <IPAddress[]> [-ComputerName <String>] [-PassThru] -NetworkId <String> [-ZoneFile <String>] [-CimSession <CimSession[]>] [-ThrottleLimit <Int32>] [-AsJob] [-WhatIf] [-Confirm] [<CommonParameters>]
Add-DnsServerStubZone [-LoadExisting] [-MasterServers] <IPAddress[]> [-ComputerName <String>] [-PassThru] [-ReplicationScope] <String> [[-DirectoryPartitionName] <String>] -NetworkId <String> [-CimSession <CimSession[]>] [-ThrottleLimit <Int32>] [-AsJob] [-WhatIf] [-Confirm] [<CommonParameters>]
Add-DnsServerStubZone [-LoadExisting] [-MasterServers] <IPAddress[]> [-ComputerName <String>] [-PassThru] [-ReplicationScope] <String> [-Name] <String> [[-DirectoryPartitionName] <String>] [-CimSession <CimSession[]>] [-ThrottleLimit <Int32>] [-AsJob] [-WhatIf] [-Confirm] [<CommonParameters>]
—————EXAMPLE 1—————
Add a file-backed stub zone
PS C:> Add-DnsServerStubZone -Name “delhi.TOSSolution.com” -MasterServers “172.23.90.123” -PassThru -ZoneFile “delhi_TOSSolution.dns”
This command adds delhi.TOSSolution.com as a file-backed stub zone. The command specifies a master server and uses the PassThru parameter to produce output
—————EXAMPLE 2—————
Add an Active Directory-integerated stub zone
PS C:\>Add-DnsServerStubZone -Name “bang.TOSSolution.com” -MasterServers 172.23.90.123 -PassThru -ReplicationScope “Forest”
This command adds bang.TOSSolution.com as a stub zone replicated to all DNS servers in the forest.
—————EXAMPLE 3—————
Add an Active Directory-integrated reverse lookup zone
PS C:\>Add-DnsServerStubZone -NetworkId 10.1.2.0/24 -MasterServers 172.23.90.124 -PassThru -ReplicationScope Forest
This command adds a stub zone for the network 2.1.10.in-addr.arpa, which is replicated to all DNS servers in the forest.
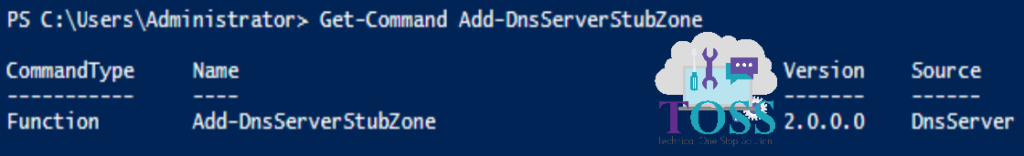
You can check the Version, CommandType and Source of this cmdlet by giving below command.
Get-Command Add-DnsServerStubZone
You can also read about
- Set-DnsServerStubZone
To know more PowerShell cmdlets(Commands) on DnsServer click here